Remote Blending
A remote blend is a blend that is not traveling on the two faces immediately adjacent to the blended edges. ACIS has various facilities for handling remote blends.
Only Some Blends Are Remote
ACIS can compute remote face-face blends or edge-face blends when they are adjacent to blends that are not remote. The following figure demonstrates a blend that has traveled onto a cylindrical preexisting blend face, which is a remote face.
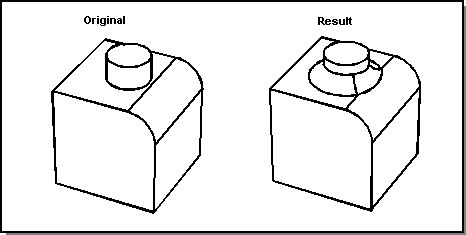
Figure. Remote Face Blend
Remote edge-face blends may also sometimes be used in a similar situation (refer to the following two figures).
All Blends Are Remote
When the blends in a sequence are all remote, then blending must determine an alternative pair of entities against which to start blending. These may result in face-face, edge-face, or even edge-edge blends. This facility is currently restricted to blend networks without vertex blends or miters.
Without remote blending, the blend shown in the following figure, would fail if the blend radius was greater than the height of the step. With remote blending, an edge-face blend is used instead.
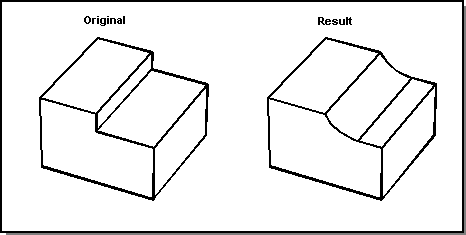
Figure. Edge-Face Blending
In the following figure, a sequence of three edge-face blends is created, as the blend radius is greater than the height of the small protrusion.
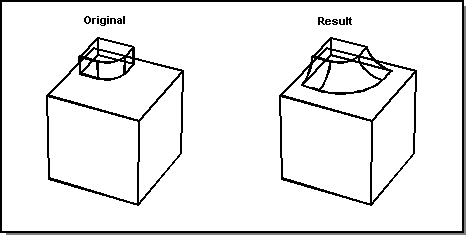
Figure. Remote Edge-Face Blending
In the following figure, a face-face blend will not fit, so the blending algorithm switches to a remote edge-edge blend.
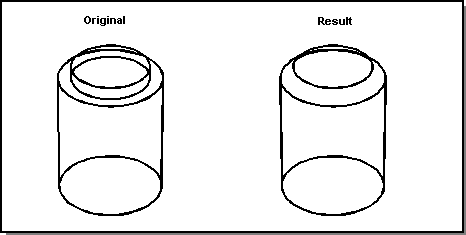
Figure. Remote Edge-Edge Blend
[Top]
© 1989-2007 Spatial Corp., a Dassault Systèmes company. All rights reserved.