name-of-option
is a string placed within quotation marks. If value is a real, it does
not require delimiters. If value is a string representing a law, it
should be enclosed in quotation marks. If value is a law, only the
variable name for the law is required. Multiple pairs of name-of-option and
value can be specified simultaneously. The available values for this
option are:
-
gap_type
-
distance
-
trim
-
overlap
-
keep_minimum_topology
-
plane_normal
-
twist_law
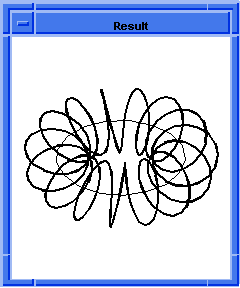
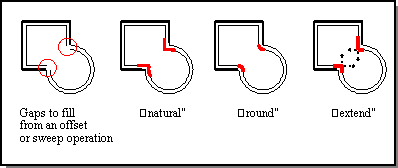
gap_type
specifies the type of gap to be placed when the offsets of adjacent,
non-tangential wire edges do not touch at a common vertex. The type can be "n",
"r", or "e" ("N", "R", "E"), which represents natural, arc, or linear gap fill,
respectively. Presently, the gap type "natural" might be done with a linear
extension if curvature extension cannot be achieved. Also the gap types
"linear" and "natural" might be done with an "arc" extension if the gap cannot
be filled by the intersection of the two extended neighboring offset curve
segments. A warning is issued if the gap_type is changed.
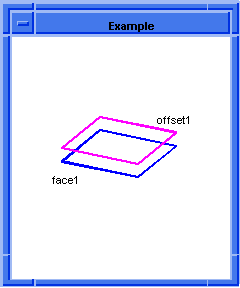
distance
can be either a double value or a law, which specifies the offset distance.
trim
is a Boolean value to indicate if self intersections are to be removed. Default
value is true.
overlap
is a Boolean value to indicate if overlapping segments are to be removed.
Default value is true.
keep_minimum_topology
is a Boolean value to indicate if additional edges are allowed in a gap fill.
Currently when filling a gap linearly or with an arc, additional edges are
added at the gap. If keep_minimum_topology is true, the additional gap fill
edges will not be added. If this leads to an unconnected offset curve, an error
will be issued. Default value is false.
plane_normal
is the option that specifies the normal vector of the wire plane, which is the
plane where the wire body lies. Because wire offset is a 2D offset, the wire
body must lie on a plane. Default value is computed plane normal by an ACIS
internal function.
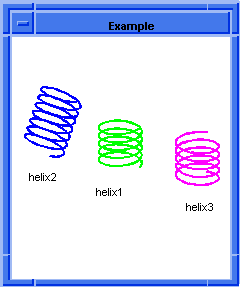
twist_law
specifies whether to use the twist law. Default value is no law (that is, no
twist); thus, the offset curve becomes simply a function of the given
offset-distance-law at the curve parameter x. In such a case and if the
offset-distance-law is a constant, the unitized cross product T x N specifies
the positive direction for the offset. If the twist-law is specified, the given
equation determines where the offset curve at curve parameter x lies in three
dimensional space. Twisting is about the tangent vector T of the wire curve and
in the plane created by T x N and N. The twist-law specifies the angle in the
TxN and N plane for the offset curve. (The twist-law evaluates to a number that
is input as radians to the cos and sin law functions.) For example, if the
offset-distance-law is the constant 2 and the twist-law is simply the law
function "x", then the result is a helix of radius 2 that winds around wire.
Note: All the options are optional, except distance,
which must be specified for a successful wire offsetting operation. If an
option is not specified, the default one is used.
options
specifies
wire_offset_options.