3D ACIS Deformable Modeling
3D Deformable Modeling is a unique interactive sculpting tool for shaping 3D models that is offered only by Spatial. Included as part of our suite of 3D modeling development technologies, 3D Deformable Modeling uses local and global editing features that allow for the easy creation and manipulation of free-form B-spline and NURBS curves and surfaces. This versatile mechanism gives you a profound level of artistic freedom when generating a precise surface.
Improves on the Standard
3D Deformable Modeling is a more powerful alternative to traditional surface modeling techniques such as control point manipulation and lofting. Control point manipulation can change a free-form shape interactively, but not while enforcing constraints. With lofting, you can build surfaces that satisfy several constraints, but it doesn't allow the sculpting of shapes. These time-consuming methods often result in surfaces with poor reflection lines and other undesirable qualities.
In contrast, 3D Deformable Modeling is intuitive, requiring less manipulation, time, and user knowledge while producing a higher-quality result.
The following sequence shows how Advanced Covering can be used to fill the missing region of a surface while maintaining both positional and tangential continuity even on geometrically complex faces.

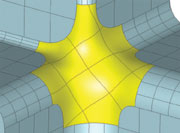
Figure. Advanced Covering with Deformable Modeling
Using an energy-based optimization strategy, 3D Deformable Modeling minimizes the energy stored due to bending and stretching. In this way, the shape that a deformable curve adopts is the one shape out of all possible shapes that minimizes the internal energy of the curve. This algorithm automatically produces fair shapes similar to those seen in the billowing of a sail or the clean line of a bending beam.
Save Time and Resources
With 3D Deformable Modeling, you can easily sculpt shapes that automatically adhere to rich sets of constraints. It allows you to perform manipulations on curves and surfaces that would otherwise be extremely difficult or impossible to accomplish using control points, saving time and resources.
Create Innovative Surfaces and Curves
Due to its precise shape and surface definition capabilities, 3D Deformable Modeling is ideal for complex mechanical jobs that require the rapid development of innovative surface and curve features, such as industrial design, aircraft skin and foil design (aerospace), automotive styling, prototype development, simulation, product design, shipbuilding, and free-form surface design for CAD/CAM/CAE and AEC applications.
Features
3D Deformable Modeling includes an extensive set of features that enable you to:
- Restrict a deformation to a limited local region.
- Make small deformations in an existing shape, which modify the shape without sacrificing its original overall characteristics.
- Create an entirely new shape by making very large deformations.
- Increase the continuity of existing shapes, quilted surfaces, or network of curves.
3D Deformable Modeling's functionality includes:
Advanced Covering Allows a surface to be fit onto circuits (collections of
edges that form closed loops) in solid or wire bodies, which is useful in
consumer product design. This feature is commonly used for end-capping,
post-translation corrections, and surface definition from curve data. Some of
the capabilities of the Advanced Covering feature include:
- Creation of non-planar, n-sided boundaries
- Retain positional and tangential continuity with adjacent surfaces
- Individual specification of boundary continuity on each edge
- Placement of auxiliary point and curve restraints (G0 only)
- Post-covering gap reporting (diagnostics)
- Specification of initial surface
- Re-covering of faces.
Full, Multi-Surface Capabilities
- Users can simultaneously deform multiple, arbitrarily trimmed surfaces.
- Advanced Control of Surface Shape
- Control position, tangency, and curvature at points and along curves. These points and curves can lie in the interior of surfaces or along surface boundaries.
- Continuity Control Along Edges
- Assign link loads to the shared edges of surfaces, allowing users to specify position (G0), tangent (G1), and curvature (G2) continuity along the edge.
Global and Local Deformations
Sculpting tools can be applied to a quilt of surfaces, constrained to deform a single surface, or even an arbitrary region of a single surface.
[Top]
© 1989-2007 Spatial Corp., a Dassault Systèmes company. All rights reserved.